With the introduction of new battery rebate programs in Queensland and the ACT this year, and a proposed rebate in NSW expected in November, the safe installation of batteries has become an increasingly important topic. A common concern among installers is determining suitable battery installation locations, particularly regarding what constitutes a habitable room and a restricted location.
The main standards that cover battery installation locations are:
- AS/NZS 5139:2019
- AS/NZS 3000:2018
- AS/NZS 4777 (for inverters)
Although these standards have specific requirements for where batteries can and cannot be placed, it’s important to use common sense when applying these rules. The main goal is to install batteries in safe locations so that in the case of a fire or explosion, it is unlikely that people will be near the battery and, if they are, they can exit the room safely.
Restricted Locations
AS/NZS 5139:2019 dictates batteries CANNOT be installed in restricted locations. Restricted locations include:
- Any restrictions as defined for switchboards (AS/NZS 3000)
- Within 600mm of any exit or entry
- Within 600mm of any vertical side of a window, or any building ventilation, opening into a habitable room
- Within 600mm of any appliance
- Within 900mm below 2, 3, and 4
- In ceiling spaces
- In wall cavities
- On roofs (except where specifically deemed suitable)
- Under stairways
- Under access walkways
- In an evacuation route or escape route.
- Within a habitable room
An exit, as mentioned above, includes garage doors. However, according to the ERAC clarification, for all states but NSW, if a person can enter/exit the garage 900mm from the battery, it can be less than 600mm from the garage door. See the ERAC clarification here for more information: https://www.erac.gov.au/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/Battery_Energy_Storage_System_02Feb2021.pdf
Habitable Rooms
A habitable room is defined as a room associated with a domestic or residential electrical installation used for normal living activities and includes:
- Bedroom
- Living room
- Lounge room
- Music room
- Television room
- Kitchen
- Dining room
- Sewing room
- Study
- Playroom
- Family room
- Home theatre
- Sunroom
Note that a garage that is used as lounge room or workspace may also be considered a habitable room. We recommend avoiding installing batteries where the homeowner might spend a considerable amount of time.
Additionally, any manufacturer clearance zones need to be maintained for batteries, inverters, and switchboards. These can vary, and you must check the manufacturer’s documentations, but a general rule of thumb is often 200-300mm on all sides of the equipment.
Recommended Battery Locations
So, considering all of these restrictions, where can a battery be installed? The best options are outside of habitable rooms if there is a suitably non-combustible material (see below) between the battery and the habitable room. Other options include, a garage, laundry, or storage room if the appropriate clearances between windows, doors, and appliances are maintained. Ancillary buildings such as a shed could also be used, but care needs to be made when considering distance from the switchboard, cable sizing/voltage drop and the necessary battery clearance values.
Non-Combustible Barriers
Materials deemed suitably non-combustible based on AS 1530.1:
- Brick or masonry block
- Concrete
- Compressed cement sheeting
- Ceramic or terracotta tiles
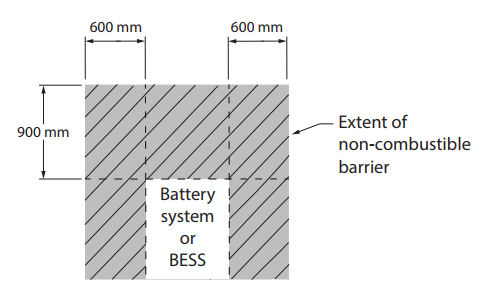
When installing the battery on a wall shared with a habitable room that is made of combustible material (e.g. wood), a non-combustible barrier must be placed between the battery and the wall. This barrier must extend 600mm to each side of the battery and 900mm above the battery even if there is a corner or a roof (so that it wraps around the corner or ceiling). We also recommend adding a non-combustible barrier if the wall is shared with a staircase or main walkway, fore example, near the front door of the house.
For examples of non-combustible barrier installations and other important information, please see the GHD Battery Booster Installation Guide.
Outdoor Installation
Please note, if you are installing a battery outside, care needs to be taken to not install it in direct sunlight. This can either be on the southern wall of the building, beneath eaves, or a fabricated shroud assuming the necessary clearances (900mm from the top) are maintained. Excessive sunlight can bring the battery temperature out of its acceptable range, voiding the warranty and creating a potentially dangerous situation due to thermal runaway of the battery.
Looking to get battery accredited and want to learn more? Check out our Grid-Connected Battery Systems Accreditation course.

