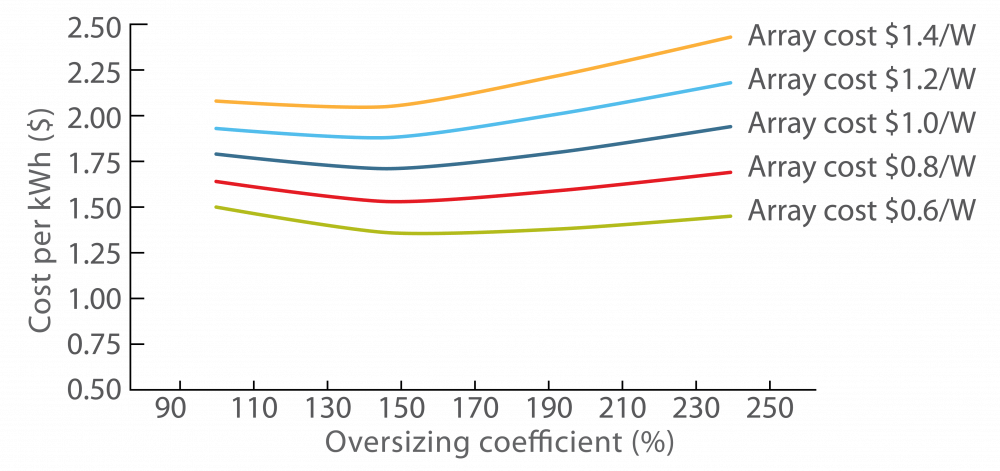
‘Array oversizing’ refers to solar photovoltaic (PV) systems that have been designed so that the solar array has a higher peak capacity than the inverter.
A solar system of a given installed capacity under irradiance consistent with Standard Test Conditions, may actually deliver up to 20% less than the nameplate rating of the solar array. This is because of the system’s and the solar modules’ losses. Oversizing the solar array has the potential to increase the system yield, as it results in a higher PV array power output during times of low irradiance (e.g. the morning and evening, and cloudy days). The recent trend of reduced cost of PV modules compared with the cost of inverters has introduced the concept of oversizing the PV array as a cost- effective method for increasing system output. The metric used to measure oversizing is known as the DC:AC ratio, array-to-inverter ratio, or simply the oversizing ratio. For example, a 3 kW inverter with an oversizing ratio of two will use a 6 kWp array.
Featured: ReNew Magazine (Issue 128), Ecogeneration Magazine (Issue 81)